Hvala unapred!
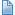
Suppose that we are given a sequence of pairs of integers, where each integer represents an object of some type and we are to interpret the pair p-q as meaning "p is connected to q." We assume the relation "is connected to" to be transitive: If p is connected to q, and q is connected to r, then p is connected to r. Our goal is to write a program to filter out extraneous pairs from the set: When the program inputs a pair p-q, it should output the pair only if the pairs it has seen to that point do not imply that p is connected to q. If the previous pairs do imply that p is connected to q, then the program should ignore p-q and should proceed to input the next pair. Figure 1.1 gives an example of this process.
Figure 1.1. Connectivity example
Given a sequence of pairs of integers representing connections between objects (left), the task of a connectivity algorithm is to output those pairs that provide new connections (center). For example, the pair 2-9 is not part of the output because the connection 2-3-4-9 is implied by previous connections (this evidence is shown at right).
3-4___3-4
4-9___4-9
8-0___8-0
2-3___2-3
5-6___5-6
2-9_________2-3-4-9
5-9___5-9
7-3___7-3
4-8___4-8
5-6_________5-6
0-2_________0-8-4-3-2
6-1 6-1




 Problem algoritama?!
Problem algoritama?!