Code:
class Test
{
void racunaj(int i, int j)
{
i *= 2;
j /= 2;
}
}
public class PozivPoVrednosti
{
public static void main(String[] args)
{
Test ob = new Test();
int a = 15, b = 20;
System.out.println("a i b pre poziva: "+a + " "+ b);
ob.racunaj(a, b);
System.out.println("a i b posle poziva: "+a+ " "+b);
}
}
class Test
{
void racunaj(int i, int j)
{
i *= 2;
j /= 2;
}
}
public class PozivPoVrednosti
{
public static void main(String[] args)
{
Test ob = new Test();
int a = 15, b = 20;
System.out.println("a i b pre poziva: "+a + " "+ b);
ob.racunaj(a, b);
System.out.println("a i b posle poziva: "+a+ " "+b);
}
}
Ovde se vrednosti promenljive a i b kopiraju u parametar (int i, int j), i svaka izmena koja se desi u metodi se odnosi samo unutar metode ? Cim se izadje iz metode promene koje su napravljanje unutar metode vise ne vaze. Ovako sam ja to shvatio..
Code:
class Test
{
int a,b;
Test(int i, int j)
{
a = i;
b = j;
}
// prosledi objekat
void racunaj(Test o)
{
o.a *= 2;
o.b /= 2;
}
void ispisiVrednosti()
{
System.out.println(" Vrednosti a: "+a+ " b: "+b);
}
}
public class PozivPoReferenci
{
public static void main(String[] args)
{
Test ob = new Test(15, 20);
// Pre prosledjivanja vrednosti
ob.ispisiVrednosti();
ob.racunaj(ob);
// Posle prosledjivanja vrednosti
ob.ispisiVrednosti();
}
}
class Test
{
int a,b;
Test(int i, int j)
{
a = i;
b = j;
}
// prosledi objekat
void racunaj(Test o)
{
o.a *= 2;
o.b /= 2;
}
void ispisiVrednosti()
{
System.out.println(" Vrednosti a: "+a+ " b: "+b);
}
}
public class PozivPoReferenci
{
public static void main(String[] args)
{
Test ob = new Test(15, 20);
// Pre prosledjivanja vrednosti
ob.ispisiVrednosti();
ob.racunaj(ob);
// Posle prosledjivanja vrednosti
ob.ispisiVrednosti();
}
}
Objekti se prosledjuju po referenci. Tako da u ovom drugom primeru parametru prosledjuje referenca (Test o).To znaci ako menjamo parametar,
menjamo i vrednost argumenta sa kojim se poziva potprogram (metoda)
Evo jos jedan primer:
Poziv po vrednosti
Code:
public class CallByValue
{
public static void main(String[] args)
{
int x = 3;
System.out.println("Value of x before calling increment() is "+x );
increment(x);
System.out.println("Value of x after calling increment()n is "+x );
}
public static void increment ( int a)
{
System.out.println("Value of a before increment is "+a);
a = a+1;
System.out.println("Value of a after incrementing is "+a);
}
}
public class CallByValue
{
public static void main(String[] args)
{
int x = 3;
System.out.println("Value of x before calling increment() is "+x );
increment(x);
System.out.println("Value of x after calling increment()n is "+x );
}
public static void increment ( int a)
{
System.out.println("Value of a before increment is "+a);
a = a+1;
System.out.println("Value of a after incrementing is "+a);
}
}
U ovom programu , promena se izvrsila na promenljivoj unutar increment(), tako da metoda nema nikakav efekat kada se izadje iz nje. Tj vrednost od X se nije promenila. Kada pozivamo po vrednosti, ta vrednost se kopira u parametar koji je definisan u metodi, i zbog toga kada se izadje iz metode ne menja se vrednost. Jer se vrednost jednostavno kopira u parametre.
Code:
class Number
{
int x;
}
public class CallByReference
{
public static void main(String[] args)
{
Number a = new Number();
a.x = 3;
System.out.println("Value of a.x before calling increment() is "+a.x);
increment(a);
System.out.println("Value of a.x after calling increment() is "+a.x);
}
public static void increment (Number n)
{
System.out.println("Value of n.x before incrementing x is: "+n.x);
n.x+=1;
System.out.println("Value of n.x after incrementing x is: "+n.x);
}
}
class Number
{
int x;
}
public class CallByReference
{
public static void main(String[] args)
{
Number a = new Number();
a.x = 3;
System.out.println("Value of a.x before calling increment() is "+a.x);
increment(a);
System.out.println("Value of a.x after calling increment() is "+a.x);
}
public static void increment (Number n)
{
System.out.println("Value of n.x before incrementing x is: "+n.x);
n.x+=1;
System.out.println("Value of n.x after incrementing x is: "+n.x);
}
}
Ovde u ovom programu svaka promena koja se izvrsi na promenljivoj x koja je deo objekta u parametru Increment() menja vrednost originalne promenljive koja je pozvana preko objekta u parametru ?
Jos da napomenem da se svi primitivni tipovi byte, short, int, long, float, double, boolean i char prosledjuju po vrednosti, a objekti se prosledjuju po referenci.
Ovu sliku i ovo objasnjenje sam nasao na jednom sajtu.
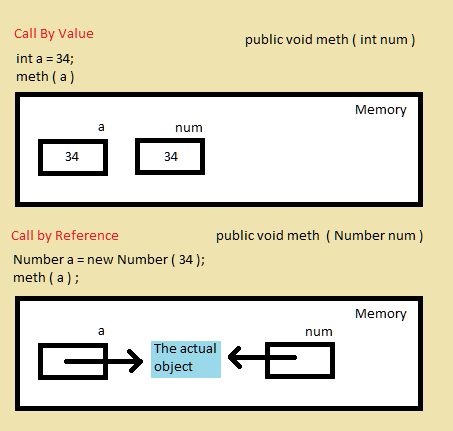
Citat:
The concept of call by reference can be better understood if one tries to look into what a reference actually is and how a variable of a class type is represented. When we declare a reference type variable, the compiler allocates only space where the memory address of the object can be stored. The space for the object itself isn't allocated. The space for the object is allocated at the time of object creation using the new keyword. A variable of reference type differs from a variable of a primitive type in the way that a primitive type variable holds the actual data while a reference type variable holds the address of the object which it refers to and not the actual object.





 Call by value i Call by reference. Razlika
Call by value i Call by reference. Razlika Re: Call by value i Call by reference. Razlika
Re: Call by value i Call by reference. Razlika